What is a DNS filter?
When someone navigates to a website, they enter a domain name, such as www.thecompany.com. However, this name is not machine-readable. Instead, a service called the Domain Name System (DNS), often referred to as the internet’s phonebook, translates the domain name into machine-readable numbers, such as 168.62.128.16. This system is the basis for the security provided by a DNS filter. A DNS filter intercepts the DNS query process, checking to see if the queried website is on an allowed or blocked list.
A DNS filter is used to:
- Prevent employees and others from navigating to malicious websites.
- Reduces the chance of a malware or ransomware infection.
- Prevents access to unsanctioned websites.
- Protects company reputation and avoids legal risk by preventing access to hate, gambling, and adult sites.
- Improves productivity.
- Improves network performance.
Challenges of DNS filters
Phishing attacks are becoming increasingly successful with the help of AI, which is empowering attackers with speed, agility, believability, and scalability. Cyber criminals use AI to craft persuasive phishing emails and corresponding phishing websites. Spoof websites can be created quickly and multiple and dynamic domain addresses can be generated. The dynamic and rapid nature of phishing websites makes it challenging for conventional DNS filters to keep pace with the changes.
The existential threat posed by AI requires a proactive and dynamic response. Conventional DNS filters utilize static blocklists based on manually configured policy lists, which are not dynamic enough to effectively handle AI-assisted phishing threats. Advanced DNS filtering utilizes AI to fight AI. Advanced DNS filtering uses machine learning algorithms, trained on a vast corpus of data points. Machine learning utilizes its training to identify emerging attack patterns and signals, enabling it to spot potentially malicious or unsanctioned websites. The DNS filter uses this intelligence to build category lists of suspicious websites. A human operator can work with the intelligence to fine-tune the blocklist.
Features of an effective DNS filter (Deployment and management)
REST API
A RESTful API allows deep integration into existing environments. A centralized dashboard enables authenticated administrators to onboard and manage customers and locations, as well as create and manage blocklists and allowlists.
On- and off-network protection
Employees must be protected whether they work from home, in the office, or travel. DNS queries must be routed through the DNS filter, even off-network. The filter must work on guest Wi-Fi to cover remote and travelling workers.
Scalability
Scales to accommodate all sizes of organizations, from small businesses to large enterprises.
Easy and rapid deployment
A cloud-based DNS filter enables fast deployment and straightforward ongoing management.
Active Directory integration
Used to streamline reporting on a per-user basis.
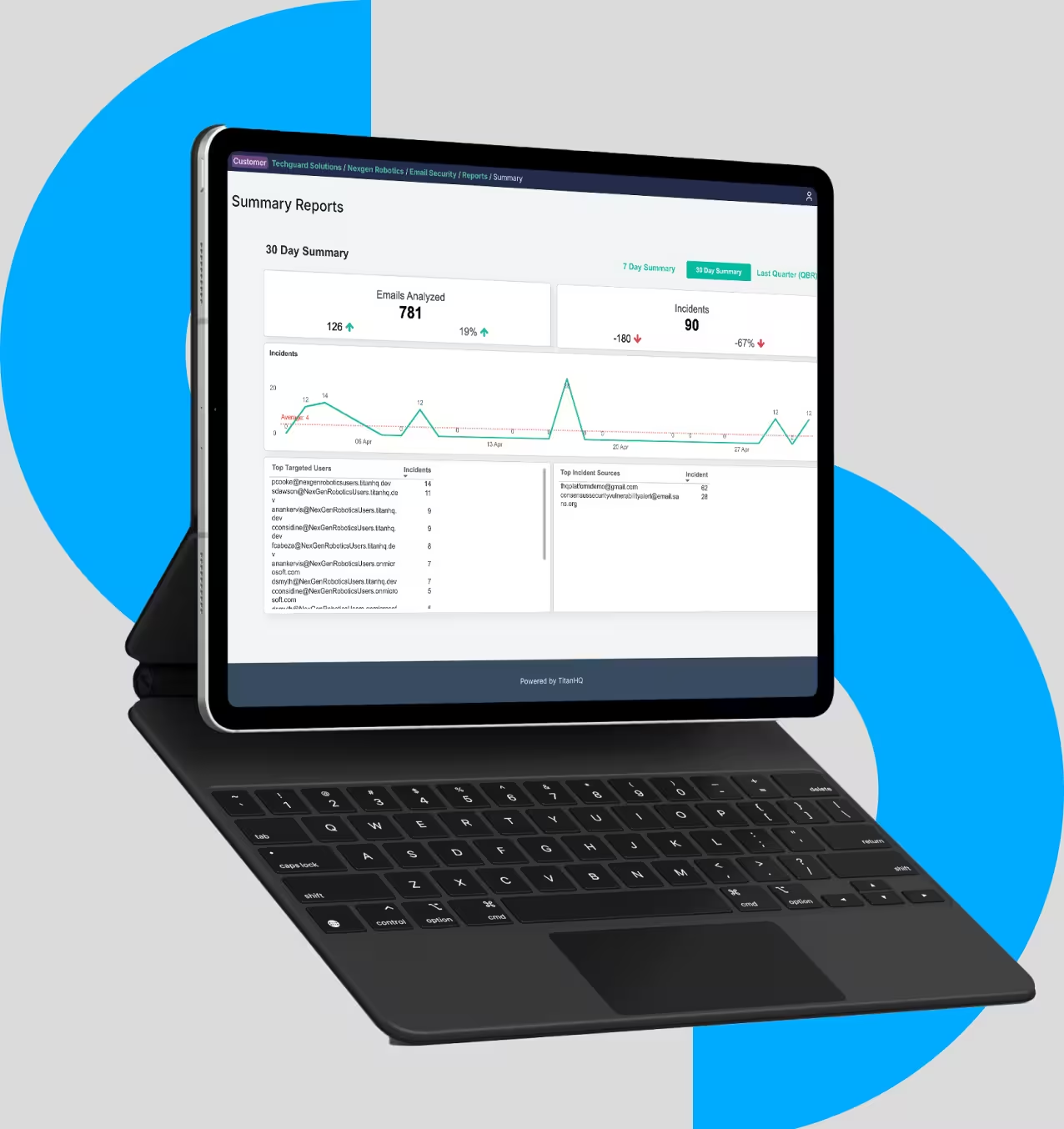
Comprehensive reporting
Comprehensive and granular reporting from a centralized dashboard.
Granular policies
Set policies and enforce on a per-user, per-IP, per-agent, and per-group basis.
Features of an effective DNS filter (Detection and policy enforcement)
Human-Supervised Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning algorithms are trained on a vast corpus of threat data that powers the AI with the intelligence to identify emerging threats. Continuous sampling ensures that the training data is current and reflects the state of the threat landscape.
Real-time analysis
DNS queries are processed in real-time to identify malicious content and prevent navigation to dangerous sites.
Categories
AI is used to generate a domain classification database. Categories include ad fraud, botnets, malware distribution, spam, phishing, cryptocurrency mining, and other malicious activities. Administrators can choose to block or restrict identified sites.
Detect “phone-home” command and control (C2C)
Cybercriminals often use C2C to send stolen data and information to a hacker. AI can help identify malicious C2C traffic that uses DNS to alert a security team of an ongoing or impending attack.
Granular to path level
The AI must be able to differentiate threat metrics at the URL, domain, and path levels.
Malicious URL revisit
Malicious URLs are constantly evolving and changing. AI-powered DNS filtering solutions must be able to rapidly inspect and detect URLs to check if the malicious category persists. Policies should be set to test malicious URLs on a set schedule.
AI-powered DNS filtering as part of a layered approach to security
Modern web-borne cyber threats are powered by AI, making them dynamic, highly scalable, and challenging to detect. Phishing websites are automatically created, and domain generation algorithms are used to change the domains used for malware attacks frequently. The level of sophistication, speed, and personalization of spoof websites requires a responsive AI-enabled approach. However, a single point solution will not suffice. Robust cybersecurity requires layers of unified AI-powered solutions to detect emerging and dynamic AI-assisted attacks. DNS filters should be part of a unified solution that includes:
Security awareness training
Combined with phishing simulations, educates and empowers users to prevent cyberattacks. Emails that slip through the net can be identified by the recipient and reported before they become an incident.
Integrated Cloud Email Security (ICES)
Advanced email security uses machine learning and natural language processing (NLP) to detect and prevent phishing emails. DNS filters and ICES are complementary solutions.
Email Backup
Secure email backup enables the fast and accurate recovery of emails and attachments in the event of a disaster, for example, during a ransomware attack. Email backup is essential for business continuity and disaster recovery.

DNS filtering for MSPs
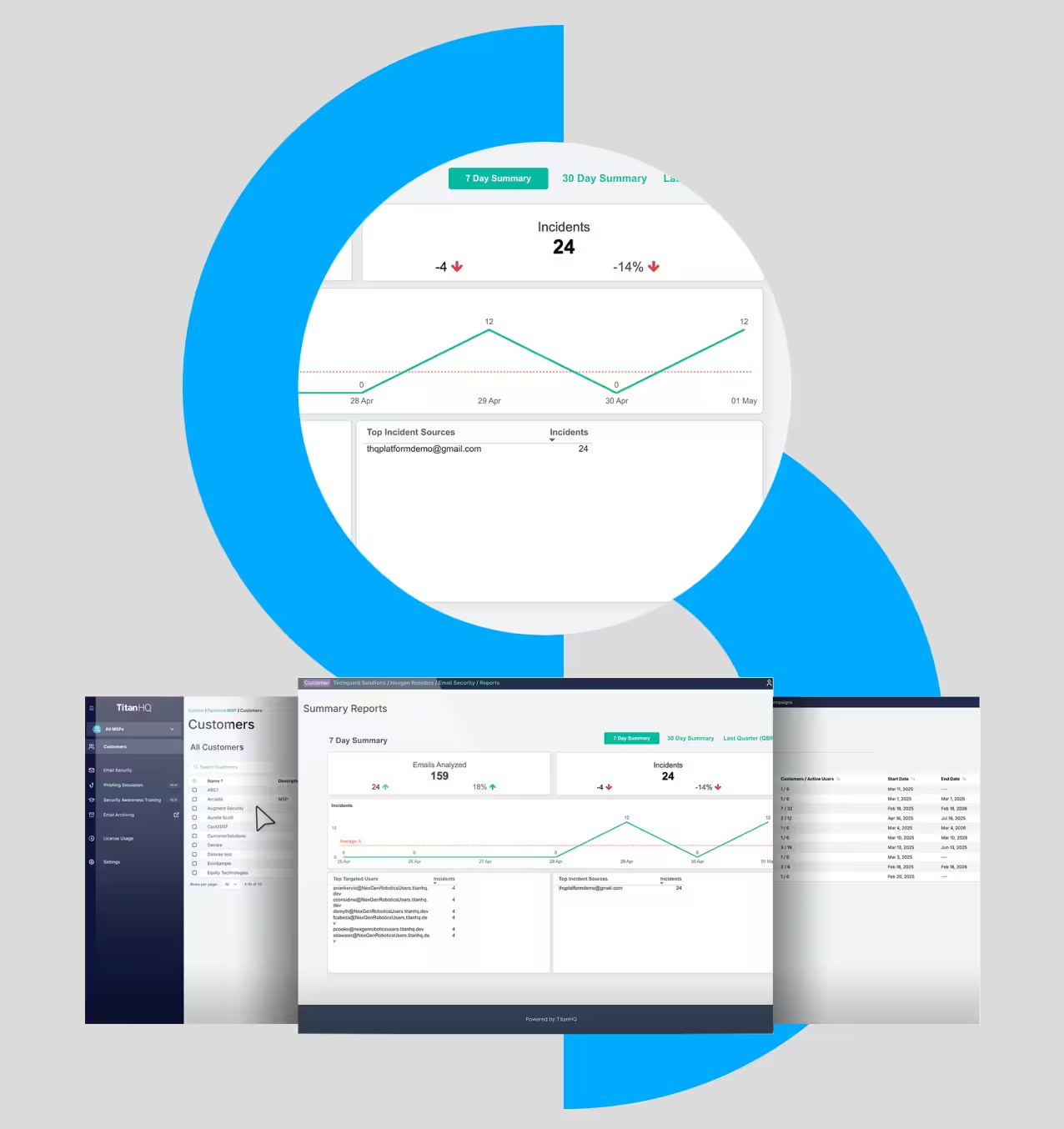
A DNS Filter is an essential aspect of modern security posture. However, conventional DNS filters can be complicated to manage, requiring continual updates to include known threats. A DNS filter should be augmented using AI to help identify emerging and dynamic phishing sites and zero-day threats. AI-powered DNS filters offer MSPs and their clients next-generation content filtering capabilities. Used as part of a unified security solution, AI-powered DNS filtering will reduce the risk an organization faces in a changing AI-driven threat landscape. An MSP should go beyond the core features of an email archiving solution to include three key capabilities:
Multi-tenant management
A centralized, cloud-based console that lets MSPs manage all customers in one place, reducing administrative overhead.
Automated protection
Fast, automated onboarding to quickly add new accounts without manual complexity.
Cross-sell readiness
Seamless bundling with Microsoft 365, Azure Blob, and Entra ID to increase value and margins.
Ready to get started?

